Everything you need to know about collagen: benefits, types and tips for selecting it

Learn more and be able to choose.
Have you noticed those little wrinkles starting to appear? Or maybe you’re feeling a little stiffness in your joints? Don’t worry, you’re not alone. These subtle signs are often the first clues to a natural phenomenon: our collagen production is decreasing.To overcome this deficit, we must help our body produce it or provide it in the form of a food supplement. But be careful, there is collagen and THE collagen and it is important to make the difference as the current market is full of references. How to choose the right product? We will help you see more clearly.
The science of collagen: the essential ally for your health
Collagen is more than just a trendy cosmetic ingredient. This structural protein makes up about 30% of our body's total protein. Think of it as the "glue" that keeps our bodies together, supporting our tissues and giving them strength.Produced primarily by cells called fibroblasts in the dermis of our skin, collagen is synthesized from essential amino acids like glycine and proline, with the invaluable help of vitamin C.
Why should we care?
Unfortunately, our collagen production naturally declines with age:- From the age of 25, it drops by around 1% per year
- At 40, we produce about 25% less collagen than at 20
- Between the ages of 20 and 70, our skin can lose up to 80% of its thickness, largely due to this loss of collagen.
This decrease is not without consequences. It can lead to:
- A loss of elasticity and firmness of the skin
- Weakening of bones and cartilage
- A slowdown in healing
- A loss of flexibility of tendons and ligaments
💡 To go further
These interconnected molecular processes collectively contribute to the progressive decline in collagen production and quality, thereby accelerating skin and tissue aging:1. Oxidative stress: Accumulation of oxidative damage alters the structure and function of collagen molecules.
2. Glycation: The formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) alters the structure of collagen, making it more rigid and less functional.
3. Decrease in growth factors: Decrease in the production of factors such as TGF-β reduces the stimulation of collagen synthesis.
4. Telomere shortening: This phenomenon affects the ability of fibroblasts to produce collagen.
How can we take action?
It is important to note that although we cannot stop this process completely, certain factors such as a balanced diet and consumption of foods rich in vitamin C, regular exercise and protection from UV rays that damage collagen fibers can help slow down the breakdown of collagen. Also, collagen supplementation is important and this is where choosing the right product becomes crucial.
Taking stock of the different types of collagen
First of all, you should know that collagen can come from a source:
• Marine: which is extracted from the skin, bones and scales of fish.
• Bovine: extracted from the skin, bones and tendons of bovines, mainly cows.
💡 Did you know? There is no such thing as vegan collagen. Collagen is an animal protein not found in the plant world. In formulas labeled "vegan", you will find mixed with other proteins (such as pea protein, a source of amino acids), collagen "boosters" such as vitamin C and/or organic silicon from horsetail, nettle or bamboo. These boosters are molecules capable of stimulating our own collagen synthesis from amino acids, most often Glycine.
In other words, the term "vegan" means that we provide boosters and all the amino acids necessary for the formation of collagen (mainly Glycine, but also Proline, Hydroxyproline and Lysine).
The different types of collagen
• Type I: This is the most abundant type of collagen in the human body, accounting for about 90% of total collagen. It is mainly found in: Skin, tendons, ligaments, bones, organs, cornea. Type I collagen is crucial for the structure and elasticity of the skin, as well as the strength of bones and connective tissues.
• Type II: This type of collagen is specific to cartilage. It helps build and maintain joint cartilage, prevent age-related joint pain, and relieve symptoms of arthritis.
• Type III: Often associated with type I, type III collagen is found in the skin (for its elasticity and firmness), blood vessels, and heart tissues. It plays an important role in cardiovascular health.
• Type IV: This type of collagen forms the basal lamina, an essential structure for endothelial cells, tissues surrounding organs, muscles and fats, and the functioning of nerves and blood vessels
• Type V: It is necessary for cell surfaces, hair and placenta.
• Type X: It is involved in bone formation and articular cartilage
How to choose THE right collagen?
With the multitude of products available on the market, knowing how to choose the right collagen is essential.
First, opt for collagen peptides: Also called hydrolyzed collagen, they are more easily absorbed by the body, especially if they are of low molecular weight (2000-2600 Daltons).
Then, choose the right type: There is no bad type of collagen, but the supplement you are going to consume must contain type I collagen. It is the most abundant in our body, representing 90% of collagen proteins. It is particularly beneficial for the skin, tendons and bones. The ideal for optimal effectiveness is to choose a product combining several types of collagen.
It is essential to check the source of the collagen:
Marine collagen may contain some undesirable substances that distinguish it from bovine collagen. The main concerns are: contamination with heavy metals such as mercury, lead or cadmium due to ocean pollution. It may also contain other pollutants such as microplastics or PCBs (polychlorinated biphenyls).
Bovine collagen generally has a lower risk of contamination by pollutants. However, it can have its own issues: a risk of transmitting animal diseases (although very low with modern purification processes) and the potential presence of hormones or antibiotics used in cattle farming.
It is important to note that these risks are generally minimized in high-quality products, which undergo rigorous purification processes and strict controls. To ensure safety, it is recommended to choose products that have been scientifically researched, certified and tested for the absence of contaminants.
Also, be careful with additives: choose pure products.
Finally, it is very interesting to consider the combination with other nutrients: Some products combine collagen with vitamin C or hyaluronic acid for synergistic effects.
A long-term investment
By taking care of your collagen intake, you are investing in your long-term health and beauty. Don't wait any longer to act and give your body the support it needs.
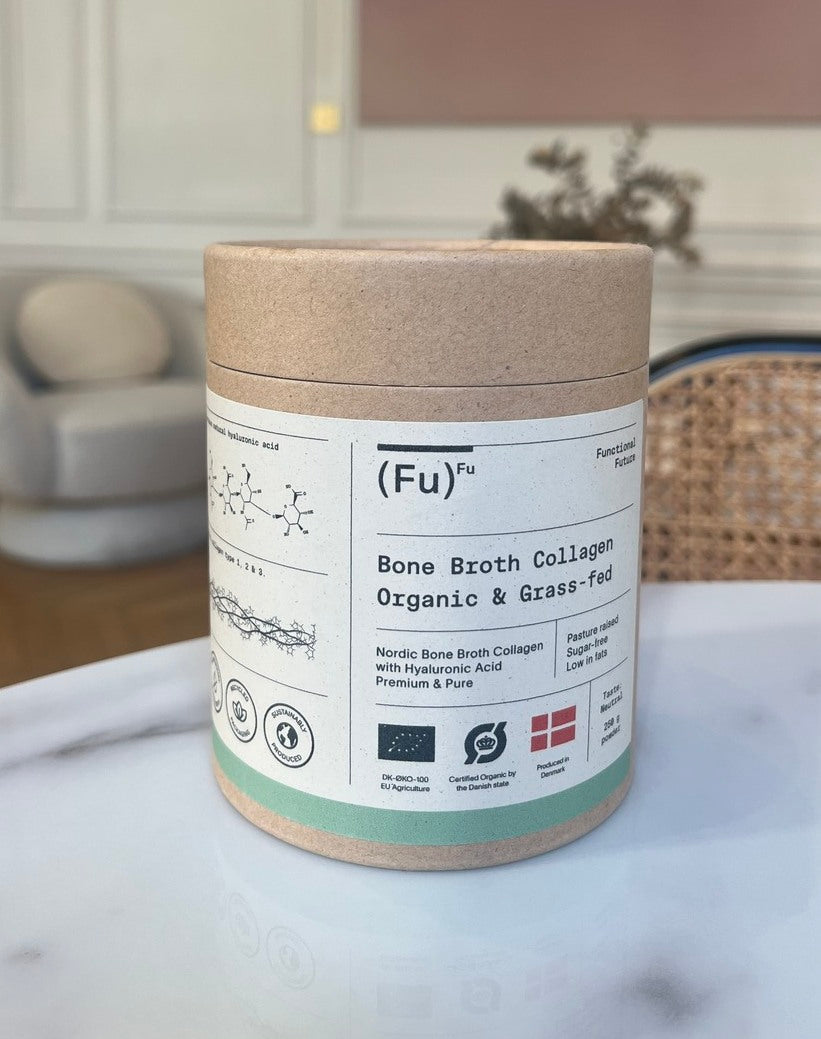
At Maison Epigenetic, we have sourced for you the “Bone broth collagen powder” from the very beautiful brand Functional Future. To find out more: click here