Intravenous Vitamin Administration: A Shield Against Intestinal Permeability
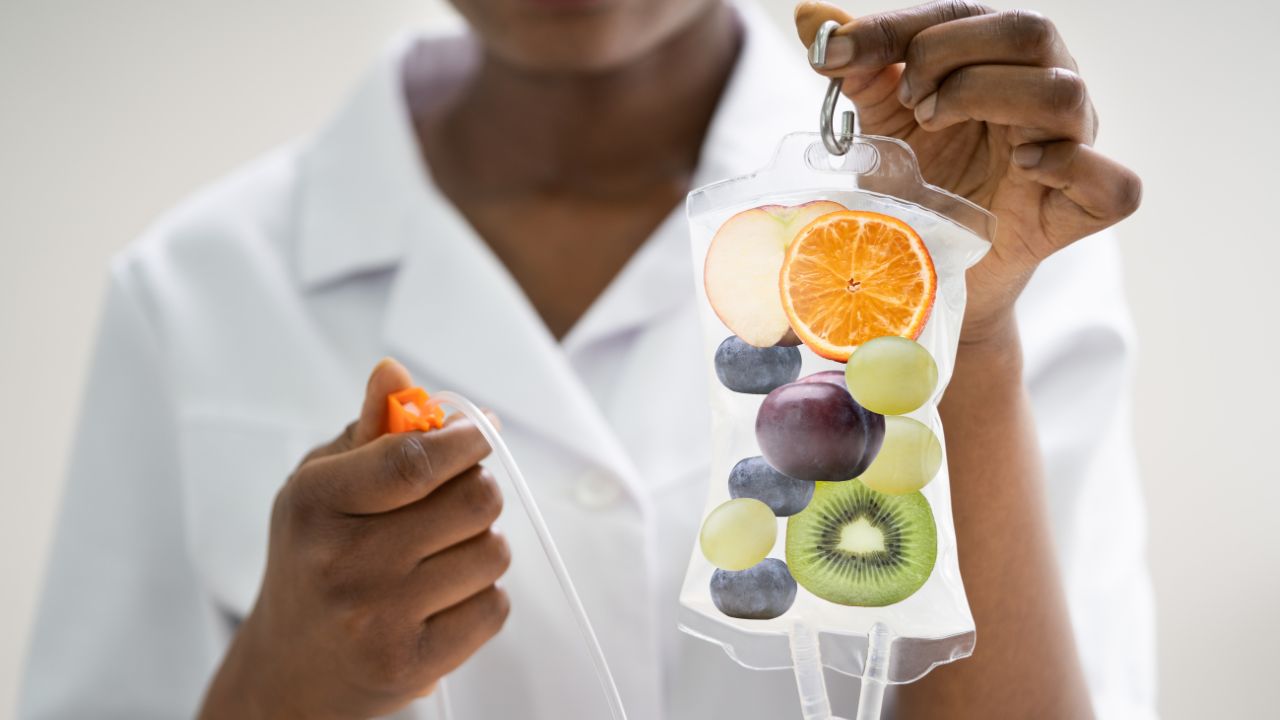

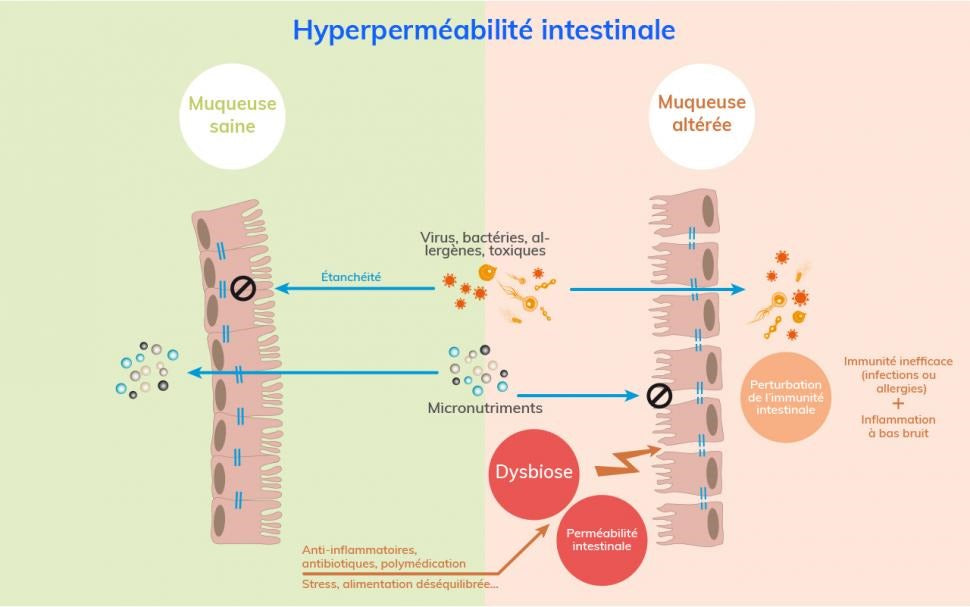
Very simply, intestinal permeability refers to the ability of the intestinal wall to control the passage of substances we bring into our body between the intestinal lumen (the inside of our intestine) and the rest of the body.
A healthy gut has selective permeability, allowing nutrients to be absorbed while preventing potentially harmful substances from passing through. When this is impaired, it is called hyperpermeability or “leaky gut syndrome.” This condition can cause toxins, allergens, and bacteria to pass into the bloodstream, causing significant health problems.
It can also cause the leakage of certain nutrients necessary for the proper functioning of our body.
It is therefore important to take care of your intestines and to be careful about what you give your body, thinking you are doing it good.
Impact of Oral Supplements on Intestinal Health
Taking oral supplements to compensate for our diets that are too poor in essential nutrients and our lifestyle can be a perilous exercise. Some dietary supplements contain additives or emulsifying agents that could have a negative impact on intestinal health.
Uncontrolled consumption can lead, for example, to:
- An overload of nutrients that can irritate the intestinal lining and affect its integrity; or
- A disruption of the delicate balance of intestinal flora that can lead to hyperpermeability.
It is important to note that judicious use of dietary supplements can be beneficial for gut health and overall health but it is crucial not to exceed recommended doses and to consult a healthcare professional before beginning any supplementation.
For people who are fragile or suffer from hyperpermeability, or who simply wish to protect their intestinal barrier, there is a way to bypass this barrier: the method of administering vitamins and minerals.
In fact, bioavailability, that is to say: the proportion of active principle which reaches the bloodstream and which becomes available for a physiological or nutritional action in our cells, depends on the method of administration of the nutrients.
The different methods of vitamin administration

Several methods of administration exist:
- The oral route which is the most common but which is subject to the limitations of intestinal absorption; but also
- The sublingual route which offers rapid absorption via the oral mucosa;
- The transdermal route which allows absorption through the skin;
- The intramuscular route, i.e. injection directly into the muscle; and
- The intravenous route, direct injection into the bloodstream which has many advantages including that of bypassing the intestinal barrier.
Focus on the Intravenous route

The intravenous route, yes, but…
Yes, because, significantly, it allows for maximum bioavailability. That is to say, the direct injection of a vitamin into the blood bypasses the digestive barriers, ensuring 100% absorption. In addition, the desired effects are almost instantaneous.
It also has a real advantage over oral administration: the ability to directly inject much higher and therefore more effective doses of vitamins and minerals into your body. It is also easier to control the exact amount administered.
Disadvantages of Intravenous Administration

But, there are indeed some disadvantages to take into consideration, the main ones being the invasive aspect and the risk of infection.
Indeed, it requires an injection, which can be apprehensive and uncomfortable for some people, but it is important to keep in mind the benefits that come from it in exchange for a little moment of discomfort, it is sometimes worth it! Concerning the risk of infection, although very low, it exists, which is why it is absolutely necessary that the preparation and administration be carried out by a qualified health professional.
There is also the cost that can be discussed. An intravenous injection of vitamins is indeed more expensive than a bottle of oral supplements.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Finally, intravenous administration of vitamins proposed for example by NADCLinic offers an effective solution to optimize absorption and bioavailability, particularly beneficial for people wishing to protect their intestinal barrier.
This method, although attractive, should not be considered as an alternative to a balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle, it is a powerful medical tool that, used wisely, can bring significant benefits. It is crucial that the choice of supplementation and the method of administration are made in consultation with a health professional who will assess your needs to offer you the mixture that will best meet your problems and deficiencies.
What do you think? Would you be willing to try it? Feel free to give us your feedback in the comments. For any questions, the Maison Epigenetic team is available to answer you.